## RMT-PPAD: Real-time Multi-task Learning for Panoptic Perception in Autonomous Driving
This repository is the official PyTorch implementation of the paper "RMT-PPAD: Real-time Multi-task Learning for Panoptic Perception in Autonomous Driving".
> [**RMT-PPAD: Real-time Multi-task Learning for Panoptic Perception in Autonomous Driving**](https://arxiv.org/abs/2508.06529)
>
> by [Jiayuan Wang](https://scholar.google.ca/citations?user=1z6x5_UAAAAJ&hl=zh-CN&oi=ao), [Q. M. Jonathan Wu](https://scholar.google.com/citations?user=BJSAsE8AAAAJ&hl=zh-CN) :email:, [Katsuya Suto](https://scholar.google.com/citations?user=x3oJXHwAAAAJ&hl=ja), and [Ning Zhang](https://scholar.google.ca/citations?hl=zh-CN&user=ZcYihtoAAAAJ)
>
> (:email:) corresponding author.
---
### The Illustration of RMT-PPAD
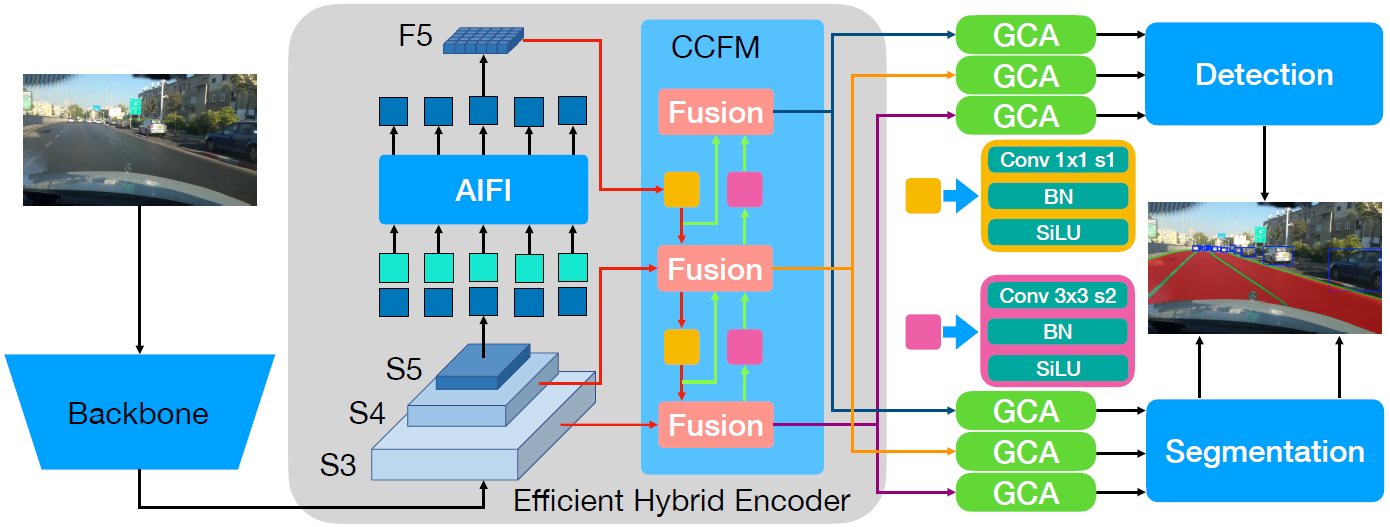
### Contributions
* We design a real-time transformer-based multi-task model (RMT-PPAD) without bells and whistles that jointly addresses object detection, drivable area segmentation, and lane line segmentation in a single network.
* We propose a lightweight GCA module, which extracts task-specific features, retains shared representations, and adaptively fuses them to alleviate negative transfer between tasks.
* We design an adaptive segmentation decoder that learns task-specific weights for multi-scale features automatically. This eliminates the need for manually designed task-specific structures while balancing fine details and global context.
* We identify the inconsistency between the lane line label widths used for training and testing in previous works. For a fair and true reflection of the model’s lane line segmentation performance, we propose a simple yet effective method to dilate the test label widths to the same as the train dataset.
* We conduct extensive experiments and ablation studies on the BDD100K dataset and real-world driving scenarios to validate the effectiveness of RMT-PPAD, which achieves SOTA performance across all tasks compared to open-source MTL models for panoptic driving perception.
### Results
Quantitative results comparison of RMT-PPAD and open-source MTL models on BDD100K
| Model |
FPS |
Params (M) |
Object Detection |
Drivable Area |
Lane Line |
| Recall (%) |
mAP50 (%) |
mIoU (%) |
IoU (%) |
ACC (%) |
| YOLOP | 64.5 | 7.9 | 88.5 | 76.4 | 89.0 | 44.0 | 79.8 |
| HybridNet | 17.2 | 12.8 | 93.5 | 77.2 | 91.0 | 52.0 | 82.7 |
| YOLOPX | 27.5 | 32.9 | 93.7 | 83.3 | 90.9 | 52.1 | 79.1 |
| A-YOLOM(n) | 52.9 | 4.4 | 85.3 | 78.0 | 90.5 | 45.6 | 77.2 |
| A-YOLOM(s) | 52.7 | 13.6 | 86.9 | 81.1 | 91.0 | 49.7 | 80.7 |
| RMT-PPAD | 32.6 | 34.3 | 95.4 | 84.9 | 92.6 | 56.8 | 84.7 |
#### Ablation study on MTL and GCA
| Methods | Recall (%) | mAP50 (%) | mIoU (%) | IoU (%) | ACC (%) |
|----------------------------|------------|-----------|----------|---------|---------|
| Object only | 92.1 | 77.5 | – | – | – |
| Drivable area only | – | – | 91.0 | – | – |
| Lane line only | – | – | – | 53.2 | 85.3 |
| Segmentation only | – | – | 91.3 | 53.3 | 85.4 |
| vanilla MTL | 92.4 | 76.9 | 91.0 | 52.4 | 83.6 |
| MTL with GCA (RMT-PPAD) | 92.1 | 78.3 | 91.3 | 52.7 | 84.1 |
Ablation Studies for segmentation performance at different confidence thresholds on toy and BDD100K.
mIoU for drivable area segmentation; IoU and ACC for lane line segmentation.
| Threshold |
Toy |
BDD100K |
| mIoU (%) |
IoU (%) |
ACC (%) |
mIoU (%) |
IoU (%) |
ACC (%) |
| 0.40 | 91.3 | 48.8 | 88.9 | 92.6 | 53.7 | 89.4 |
| 0.45 | 91.3 | 49.2 | 88.7 | 92.6 | 54.0 | 89.1 |
| 0.50 | 91.1 | 49.6 | 88.4 | 92.4 | 54.3 | 88.9 |
| 0.55 | 90.9 | 50.0 | 88.2 | 92.1 | 54.6 | 88.7 |
| 0.60 | 90.4 | 50.3 | 87.9 | 91.7 | 55.0 | 88.4 |
| 0.65 | 89.8 | 50.6 | 87.5 | 91.0 | 55.2 | 88.1 |
| 0.70 | 89.0 | 51.0 | 87.2 | 90.3 | 55.5 | 87.7 |
| 0.75 | 88.1 | 51.4 | 86.7 | 89.5 | 55.9 | 87.3 |
| 0.80 | 87.1 | 51.8 | 86.2 | 88.5 | 56.3 | 86.8 |
| 0.85 | 85.9 | 52.3 | 85.4 | 87.4 | 56.6 | 86.0 |
| 0.90 | 84.2 | 52.7 | 84.1 | 85.9 | 56.8 | 84.7 |
| 0.95 | 80.9 | 52.1 | 81.0 | 83.4 | 55.8 | 81.5 |
**Notes**:
- The works we have used for reference include `YOLOP`([paper](https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11633-022-1339-y),[code](https://github.com/hustvl/YOLOP)), `HybridNets`([paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2203.09035),[code](https://github.com/datvuthanh/HybridNets)), `YOLOPX`([paper](https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S003132032300849X),[code](https://github.com/jiaoZ7688/YOLOPX)), `A-YOLOM`([paper](https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10509552),[code]([https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics](https://github.com/JiayuanWang-JW/YOLOv8-multi-task))). Thanks for their wonderful works.
---
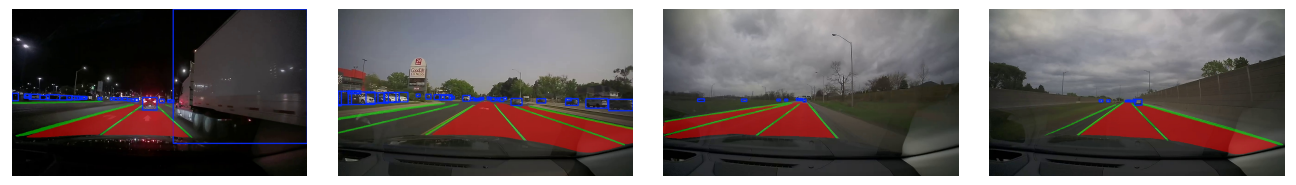
### Visualization
#### Real Road
---
### Requirement
This codebase has been developed with [**Python==3.8.19**](https://www.python.org/) with [**PyTorch==2.4.1**](https://pytorch.org/get-started/locally/).
```setup
cd RMT-PPAD
conda env create -f environment.yml
conda activate RMTPPAD
cd ultralytics
```
### Data preparation and Pre-trained model
### Note:
Since we extended the label size for lane line testing, please use our provided dataset to reproduce the results reported in the paper. Further details are described in the paper.
#### Download
- Download the images from [images](https://bdd-data.berkeley.edu/).
- Pre-trained model: [RMT-PPAD](https://uwin365-my.sharepoint.com/:u:/g/personal/wang621_uwindsor_ca/EVvXPuqxXdRAkIuAVdth14gBYKuDJ6XqlA2ppRHsmeQN_w?e=hKcXJX).
- Download the annotations of detection from [labels](https://uwin365-my.sharepoint.com/:u:/g/personal/wang621_uwindsor_ca/EV2FyiQg0llNpBL2F5hnEi0BwfEFTP3jckw7adfLSXPzrQ?e=jSaTOO).
- Download the annotations of lane line segmentation and drivable area segmentation from [mask](https://uwin365-my.sharepoint.com/:u:/g/personal/wang621_uwindsor_ca/EXrUtDWQ5vlAgzaGopIC3foBZXbs5JNNJRgvR4XotO2cgg?e=CVLOHg).
We recommend the dataset directory structure to be the following:
```
├─dataset root
│ ├─images
│ │ ├─train2017
│ │ ├─val2017
│ ├─labels
│ │ ├─train2017
│ │ ├─val2017
│ ├─mask
│ │ ├─lane
│ │ │ ├─train2017
│ │ │ ├─val2017
│ │ ├─drivable
│ │ │ ├─train2017
│ │ │ ├─val2017
```
Update the your dataset path in the `./ultralytics/datasets/bdd-multi.yaml`.
### Training
You can set the training configuration in the `./ultralytics/yolo/cfg/default.yaml`.
```
python train.py
```
You can change the setting in train.py
### Evaluation
You can set the evaluation configuration in the `./ultralytics/yolo/cfg/default.yaml`
```
python test.py
```
You can change the setting in test.py
### Prediction
```
python predict.py
```
You can change the setting in predict.py
## Citation
If you find our paper and code useful for your research, please consider giving a star :star: and citation :pencil: :
```BibTeX
@ARTICLE{2025arXiv250806529W,
author = {{Wang}, Jiayuan and {Wu}, Q.~M. Jonathan and {Suto}, Katsuya and {Zhang}, Ning},
title = {RMT-PPAD: Real-time Multi-task Learning for Panoptic Perception in Autonomous Driving},
journal = {arXiv e-prints},
keywords = {Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Machine Learning},
year = 2025,
month = aug,
eid = {arXiv:2508.06529},
pages = {arXiv:2508.06529},
archivePrefix = {arXiv},
eprint = {2508.06529}
}
```